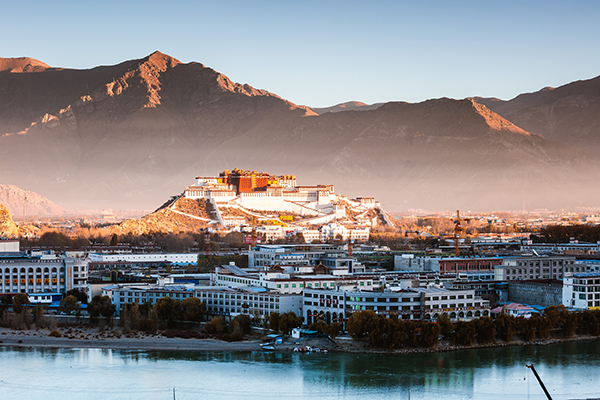
Tibet moves forward with cultural preservation
Updated: 2022-04-21 (chinadaily.com.cn)  Print
Print 
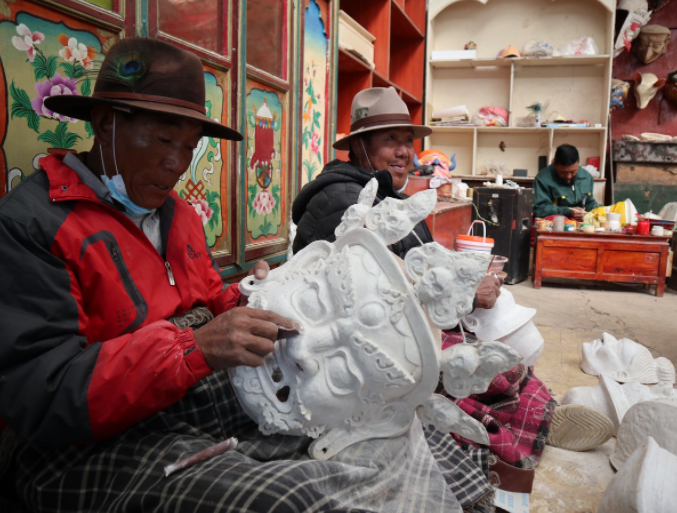


Tibetan workers create masks in Dagze county of Lhasa, Southwest China's Tibet autonomous region. [Photo by Palden Nyima/chinadaily.com.cn]
The Tibet autonomous region achieved remarkable results in 2021 on traditional cultural inheritance and protection, an official said at a work conference recently in Lhasa, the capital.
Seventeen national intangible cultural heritage representative projects were added, and the first regional level cultural and ecological protection work was launched.
Xiao Chuanjiang, deputy head of Tibet's cultural department, noted that the region began protecting ancient books and documents related to the Potala Palace and that the palace finished a survey of more than 4,500 volumes of ancient books, restored more than 21,900 pages of damaged ancient books and converted more than 350 volumes of ancient books into e-books for public reading.
"At the same time, with the cultural relics protection work, we finished investigating 277 sites of grotto temples or cliff images and carried out 23 archaeological excavation projects," Xiao said.
Of the excavations in 2021, the Sangsdar Lungmgo gravesite discovered in Ngari prefecture was ranked among China's 10 most important archaeological finds of 2020, and the Damshung cemetery site in Damshung county was selected as one of the Top 10 new archaeological discoveries of 2021, he said.
"Last year, we also completed the protection scope and construction control zones at 15 national sites and 518 cultural relics protection sites," he said.








